It’s a phrase we’ve all heard: prevention is better than cure. This wisdom, often reserved for health, also finds an apt analogy in project management – specifically in Quality Control (QC). Much like a proactive approach to health takes care of the body, QC protects projects from avoidable setbacks. Learn about Quality Control in construction, understand ways of implementing it and discover the critical benefits QC delivers to all key stakeholders.
What is Quality Control in Construction Project Management?
In the high-pressure world of construction, Quality Control ensures projects meet desired standards, mitigates risks and optimises efficiency. QC encompasses the processes and techniques used to verify that project deliverables align with predefined quality benchmarks. It ensures compliance with client expectations, safety standards, legal requirements and budgetary constraints, significantly contributing to project’s overall success.
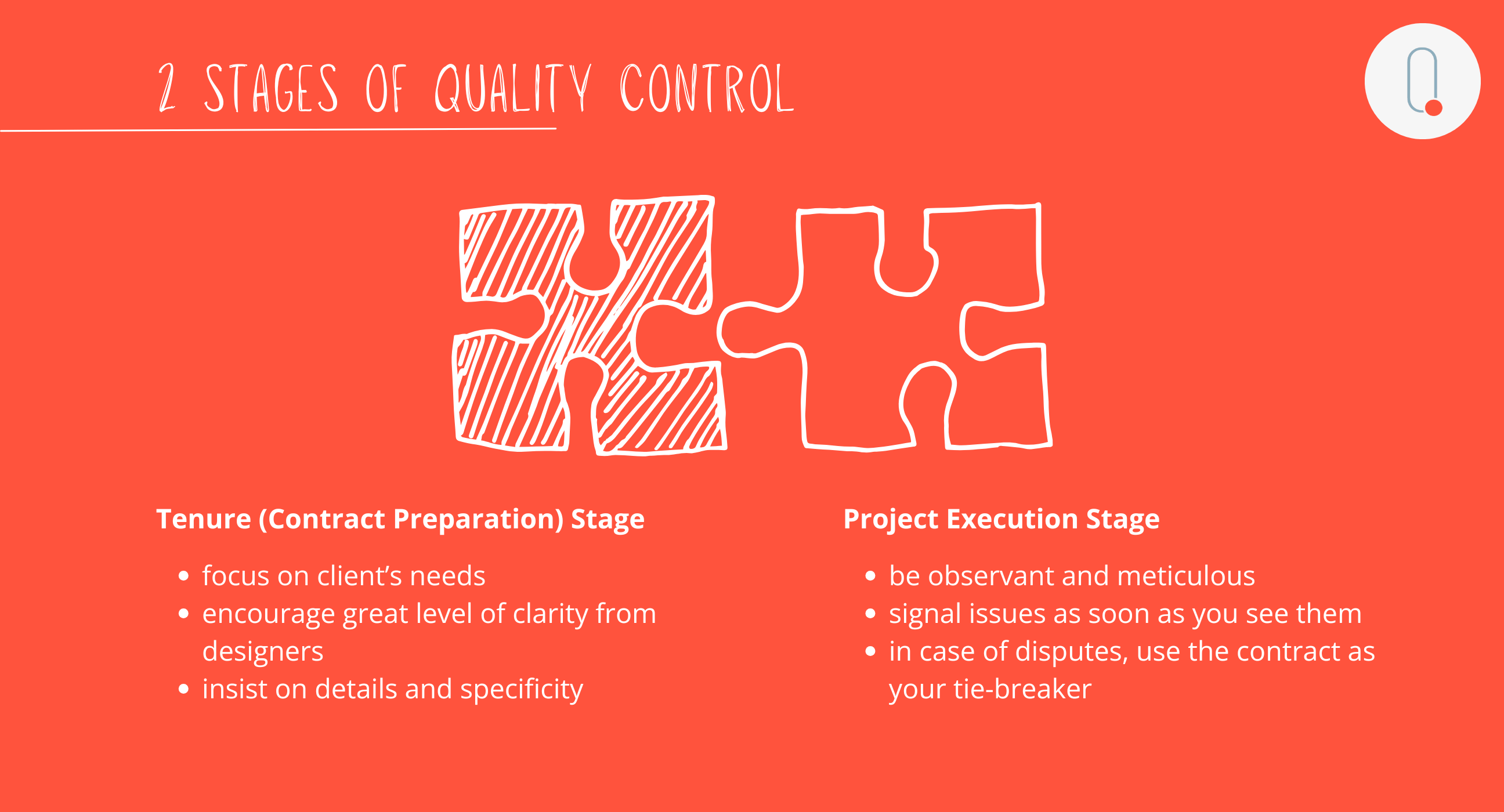
The Two Stages of QC
Quality Control consists of two key stages: the planning and contract preparation phase and the project execution phase. Looking at it from this perspective, there is a natural milestone separating the two stages, and that is the contract signing.
Stage 1: Planning and Contract Preparation Phase
A robust QC strategy begins long before the first shovel hits the ground. During this phase, the tender document establishes clear and detailed quality standards and criteria. These benchmarks serve as the backbone of the project, guiding every stage from design to completion.
We see it time and time again – the tender stage of the project is crucial but often neglected. Yet this stage lays the foundation for quality, enabling significant time and cost savings. A well-structured contract acts as a preventative measure: it allows for the execution (or enforcement) of expected quality, creating immunity to common threats and issues.
This is why in our approach, we take customer’s needs as the starting point and then work very closely with designers. We work with them to develop concepts, engage with specifications and demand clarity and an appropriate level of detail.
Stage 2: Project Execution Phase
Once construction begins, QC shifts to proactive monitoring and intervention. During this stage, it’s important to be observant and meticulous, flagging all aberrations from the originally agreed scope before they become an issue. The earlier the potential problem is discovered, the sooner it can be mitigated or avoided.
If you’ve done your homework, and your contract is clear and detailed, it seamlessly transforms major quality disputes into manageable conversations. When problems arise, they are often addressed faster and with greater ease if clear contract conditions are in place.
Disputes, while sometimes inevitable, are best resolved through collaboration rather than escalation and legal recourse is usually a last resort. Effective change management, contract administration and stakeholder communication are invaluable in helping this to be the case.
Why is Quality Control Crucial?
The importance of QC goes beyond merely delivering a functional building. Its reach extends across every stage of a project, offering advantages such as:
Customer Satisfaction
Clients expect their project to materialise as envisioned. Effective QC ensures these expectations are met, preventing disappointment and fostering trust. For example, achieving a specified exterior finish may require rigorous QC and market research to align outcomes with the client’s expectations.
Lower Project Risks
Quality Control identifies potential issues early, preventing minor concerns from becoming costly setbacks. For instance, discovering a misaligned foundation during early inspections allows for swift correction, ensuring the integrity and timescales of the entire project.
Legal Compliance
Construction projects must adhere to numerous regulations, including building codes, safety standards and environmental laws. Qualtiy Control ensures such compliance, mitigating the risk of fines, delays, or reputational damage.
Improved Efficiency
Integrating QC from the outset reduces rework, minimises waste and optimises resource use. For example, identifying unsatisfactory room layouts early on prevents redesign, installation delays and rework.Time management is different though. It is a PM’s job to keep it in check and flag potential threats of project going overtime as well as ensuring that those hazards get accounted for or resolved.
Integrating Quality Control with Project Management
It’s worth keeping in mind that Quality Control is not a standalone process; it must be seamlessly integrated with other project management tasks and skills, including risk management, scheduling and communication. This holistic approach ensures coordination, significantly reduces risks and keeps the project aligned with broader objectives.
Building Client Trust and Satisfaction
As mentioned before, for clients, QC is more than technical; it is assurance of reliability and professionalism. Consistently meeting quality standards strengthens trust and enhances client satisfaction. A project delivered on time and within budget is a testament to the team’s competence, creating opportunities for repeat business and referrals. There aren’t very many better customer retention strategies than this!
By identifying and resolving issues early, QC also saves time and money. This efficiency bolsters client confidence in the team’s ability to deliver high-quality outcomes.
”If you’ve done your homework, and your contract is clear and detailed, it seamlessly transforms major quality disputes into manageable conversations.
Common Challenges in Implementing Quality Control in projects
While the benefits of Quality Cotnrol in Project Management are clear, its implementation is not without challenges. Here are some common obstacles and strategies to overcome them:
Defining Clear Standards
The definition of "quality" can vary significantly among stakeholders. Misalignment can lead to disputes and dissatisfaction. Early collaboration to establish clear, measurable standards ensures everyone is on the same page, reducing the likelihood of conflicts.
Time and Resource Constraints
QC processes require time and resources, which may be difficult to manage under tight deadlines. Prioritising critical checks and streamlining processes can help maintain quality without compromising schedules.
Training and Team Engagement
QC’s success relies on a well-trained and engaged team. Regular training sessions and refresher courses on quality standards, legal requirements and tools ensure alignment with project objectives.
Maintaining Consistency
Large projects with multiple teams face the challenge of ensuring consistent quality. Regular site inspections, standardised procedures and clear communication help maintain uniformity. Documenting processes and updating all team members on quality benchmarks ensures consistent execution.
The Prescription for Success
Quality Control is more than just a mitigation strategy; it’s one of the pillars of construction project management. It ensures deliverables meet client expectations, enhances efficiency, reduces risks and supports a strong industry reputation.
Much like a well-considered health plant prevents illness, a robust QC system protects projects from costly mistakes. The long-term benefits of reliable, safe and high-quality outcomes make QC an indispensable element of success in construction.
It’s a prescription every project should fill in immediately.